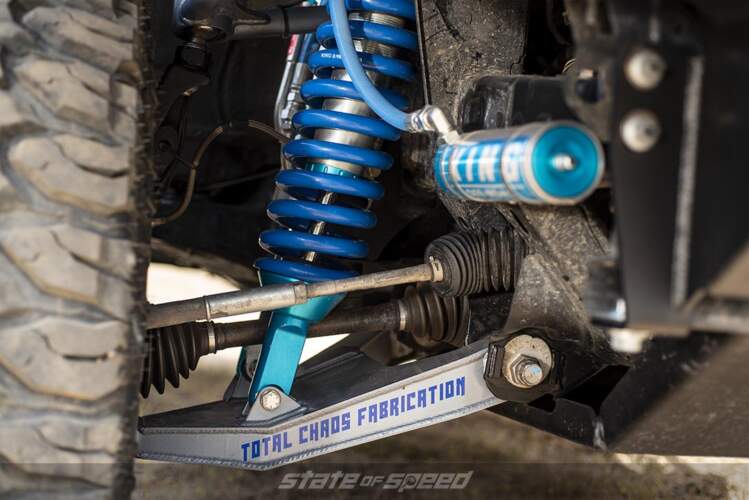
Suspension Tech: Shock Reservoirs and Bypass Valves
Performance hydraulic shocks are both simple, and complicated at the same time. Both their function, and the parts they use are relatively simple, but it’s how they are configured that makes such a huge difference. First let’s look at what shocks do. The weight of the vehicle is held up by some type of spring (air, leaf, coil, or torsion bar). The shocks control the motion of the suspension. They do this by friction which causes heat. In essence, they do the same thing that your brakes do, but differently.

Tires: Milestar Patagonia M/T – 38X13.50R17LT
Hydraulic shocks are filled with special fluid that comes in different viscosities. Viscosity is a technical term for how thick, or thin the fluid is. The shock has a body, a shaft, and a piston. The piston is mounted to the end of the shaft which slides inside the bore of the shock body. As the shock is extended or collapsed, the shock fluid inside the body of the shock is forced through openings (ports) in the piston. These openings are covered by flat springs or shims that flex to either open or close the ports. As the fluid flows through the ports, it creates friction, and therefore heat, so it dissipates energy. This is commonly referred to as damping. The heat is then transferred to the air outside the shock. Shocks use thermodynamics, and fluid dynamics to control the movements of your suspension. Like I said, they are both simple, and complicated at the same time.

Tires: Milestar Patagonia M/T – 40×13.50R17LT
Most factory supplied shocks, and inexpensive aftermarket shocks, have no external features. The common name for these shocks are smooth bodies, and it’s one reason why they are inexpensive. They still work the same way as the expensive shocks do, by forcing fluid through the ports in the piston. As the shaft moves in and out of the shock body, the piston moves through the fluid, and the shaft displaces the fluid. There needs to be room in the shock body for that shock fluid to go. On some shocks, they just leave enough air space for the fluid to move. If you are in rough terrain, and the shaft is moving in, and out quickly, the air in the shock body can mix with the fluid reducing the viscosity; creating emulsification. This causes the shock to fade. It can no longer provide the same damping. Your shocks will not be as effective until they cool down, and the air and fluid separate again. To prevent this, some shocks have a floating piston that separates the fluid, and the air. This prevents the fluid from foaming, but it takes up room in the shock. If you are using the factory supplied shock mounting locations, this will limit the amount of travel available for the shock to cycle.

Tires: Milestar Patagonia M/T – 315/70R17LT
Most factory supplied shocks, and inexpensive aftermarket shocks, have no external features…
Once you start moving up in price levels, you will see external features like remote reservoirs, and bypass tubes. Both of these features are used to allow additional flow of the fluid inside the shock. Remote reservoirs can be attached to the shock body, or be mounted remotely by using a hose between the shock body, and the reservoir. For added strength, shock manufacturers will increase the diameter of the shock shaft. This then displaces even more fluid. With a remote reservoir, you have the necessary space to allow the additional fluid to be displaced, and you can add additional features that are not typically found on smooth body shocks. Most remote reservoirs have a floating piston, and a valve that allows you to charge the reservoir with compressed nitrogen. Nitrogen is used because it is more stable than oxygen; it expands less when it gets hot. This nitrogen pressure forces the floating piston against the shock fluid so no air bubbles form in the shock fluid. Increasing the nitrogen pressure can also be used as a minute tuning adjustment, but that’s a whole other article. Since fluid is moving from the shock body to the reservoir, some shocks will have an adjuster that controls that flow of fluid. It is one more opportunity to create adjustment to the shock. It allows you to change the damping of the shock by simply turning a knob. You can stiffen them up to control sway on the street, and then back them off so your suspension will travel freely when in the dirt.
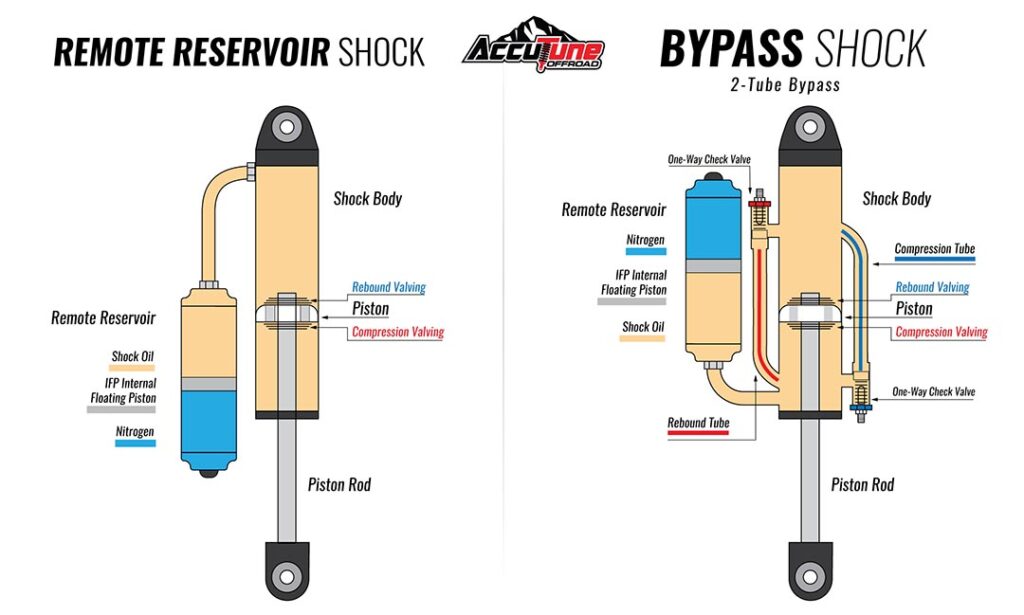
When it comes to the ultimate in adjustability, you now have the bypass shock. There are internal, and external bypass shocks. Fluid bypass works on both the compression stroke (the shaft pushing into the shock body) and the rebound cycle (the shaft pulling out). First we will talk about a single, external bypass tube used in compression, and what it does. The bypass tube will be welded to the outside of the shock body. It has an intake port that allows fluid in, and an adjustable, one way valve on the opposite end of the tube that regulates fluid flow back into the shock body. As the piston moves during compression, it pushes fluid into the bypass tube. Depending on the way the valve is adjusted, it could be a lot of fluid, or very little. The more fluid through, the softer it will be, and vice versa.
Now we can discuss what it means to be position sensitive. Let’s say you have 3 bypass tubes that work during the compression cycle, and the shock is completely extended. As the piston moves into the shock body it is pushing fluid into all three bypass port openings. The openings are strategically placed on the shock so each opening creates a zone. As the piston moves past an opening, no more fluid is moving through that tube. Depending on where the ports are located in the stroke, you can adjust the fluid flow according to the position of the piston. That makes the bypass ports position sensitive. You can make the shock progressively stiffer as it compresses, or several other configurations according to bypass tube placement, and number. The same is possible for the rebound cycle.
When it comes to the ultimate in adjustability, you now have the bypass shock…
When it comes to bypass shocks, there is also an internal bypass configuration that uses port openings that are not typically externally adjustable. The internal bypass design has a sleeve inside the body where the piston rides. The sleeve has ports in it to allow fluid to flow through to the space between the sleeve, and the larger diameter of the actual shock body.

Tires: Milestar Patagonia M/T – 37X12.50R17LT
We have only covered the basics of bypass, and external reservoirs. There are many different variations and unique applications to these basic concepts. When it comes to shock design, the best and the brightest have been experimenting for over a century. When it comes time to upgrade your shocks, be sure to talk to the experts at the shock companies as technology, and designs continue to advance. Both Fox, and Bilstein are making electronically controlled shocks that are even more intricate, and capable of fine adjustments.







